HStack
func HStack(
alignment: VerticalAlignment = .center,
spacing: CGFloat = 0,
@FastArrayBuilder<Element> children: () -> [Element]
)
HStack arranges child elements horizontally and acquires the size of all children.
var body: Layout {
HStack {
icon
label
Spacer()
}
}
Alignment
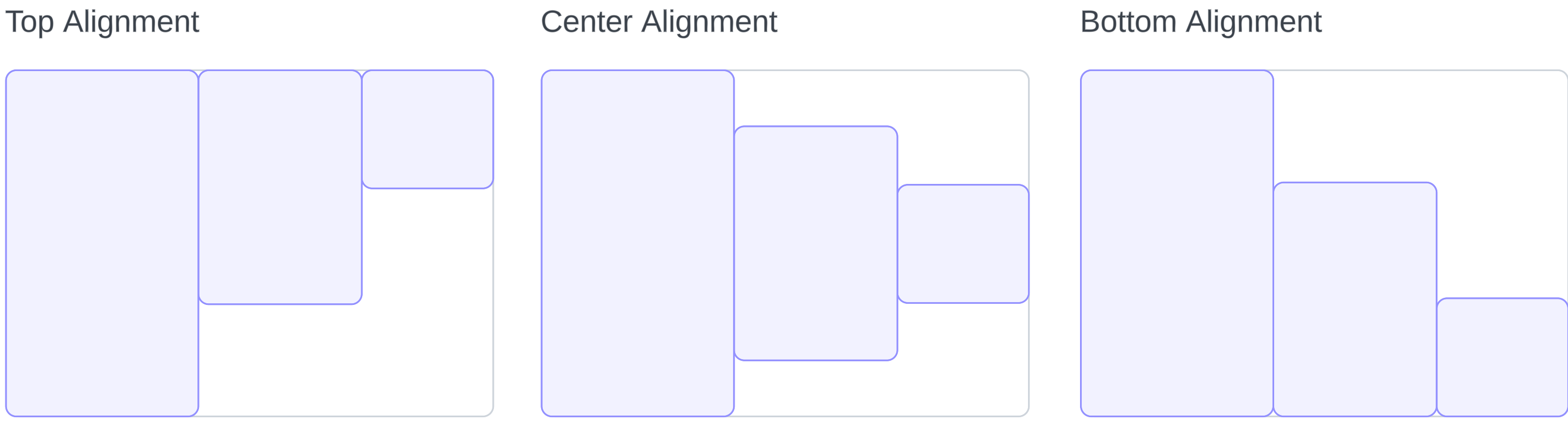
You can control alignment of elements within stack with the alignment parameter:
var body: Layout {
HStack(alignment: .top) {
view1
view2
view3
}
}
Spacing
A fixed amount of spacing can be added between every element via spacing parameter:

var body: Layout {
HStack(spacing: 8) {
view1
view2
view3
}
}
Spacer
Spacer() can be used to specify flexible spacing. The example below adds a flexible spacer between two views that pushes them apart:

var body: Layout {
VStack {
view1
Spacer()
view2
}
}
Spacer(x) can be used to add fixed spacing between views.

var body: Layout {
VStack {
view1
Spacer(8)
view2
Spacer(8)
view3
}
}
Performance Considerations
Up to two measurements may be performed to determine the size of certain child elements. Fixed-size elements (e.g., .frame() or UIImage) are measured only once. Fully flexible elements are not measured directly; instead, they are assigned a size based on the available space, which is proportionally distributed among all fully flexible views.
If a stack contains two or more partially flexible views (e.g., UILabel) and the proposed size is smaller than the intrinsic content size, the child elements may be measured multiple times. A common indication of double measurements in a HStack is line break in multiline text or truncation in single line text. When the proposed size is infinite, no double measurement occurs.
To avoid double measurement, use .layoutPriority() modifier to specify the order in which child elements should be measured.